Mechanism of Disease
Not an actual patient. Individual results will vary.
Autoinflammatory vs autoimmune disease
Autoinflammatory diseases like Still’s disease are primarily reliant on the IL-1β pathway, while autoimmune diseases feature arthritic symptoms and are caused by different pathways.1-5
IL-1β is a central driver in Still’s disease1,6,7
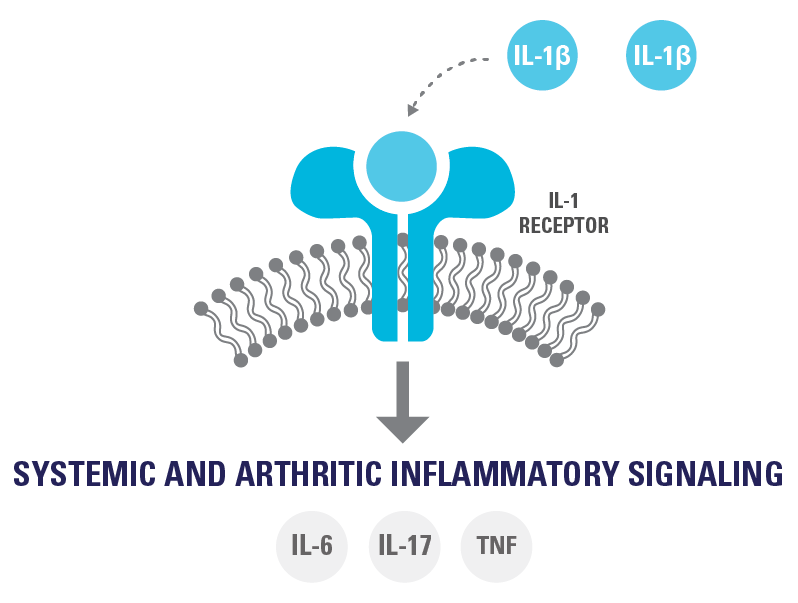
IL-1β lies at the center of Still’s disease, driving broad arthritic and systemic manifestations.8-11
Illustration is not a comprehensive depiction of all downstream pro-inflammatory cytokines activated through IL-1β in Still’s disease.
Downstream effects of IL-1β may lead to spiking fever, rash, arthritis, macrophage activation, leukocytosis, and hepatosplenomegaly6,8
References: 1. Lachmann HJ, Quartier P, So A, Hawkins PN. The emerging role of interleukin-1β in autoinflammatory diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(2):314-324. doi:10.1002/art.30105 2. Dinarello CA. A clinical perspective of IL-1β as the gatekeeper of inflammation. Eur J Immunol. 2011;41(5):1203-1217. doi: 10.1002/eji.201141550 3. Ding Q, Hu W, Wang R, et al. Signaling pathways in rheumatoid arthritis: implications for targeted therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):68. doi.10.1038/s41392-023-01331-9 4. Pisetsky DS. Pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023;19(8):509-524. doi:10.1038/s41581-023-00720-1 5. Warrington R, Watson W, Kim HL, Antonetti FR. An introduction to immunology and immunopathology. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2011;7(suppl 1):S1. doi:10.1186/1710-1492-7-S1-S1 6. Macovei LA, Burlui A, Bratoiu I, et al. Adult-onset Still’s disease—a complex disease, a challenging treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;23(21):12810. doi: 10.3390/ ijms232112810 7. Lopalco G, Cantarini L, Vitale A, et al. Interleukin-1 as a common denominator from autoinflammatory to autoimmune disorders: premises, perils, and perspectives. Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:194864. doi: 10.1155/2015/194864 8. Rossi-Semerano L, Koné-Paut I. Is Still’s disease an autoinflammatory syndrome? Int J Inflam. 2012;2012:480373. doi:10.1155/2012/480373 9. Jamilloux Y, Gerfaud-Valentin M, Martinon F, Belot A, Henry T, Sève P. Pathogenesis of adult-onset Still’s disease: new insights from the juvenile counterpart. Immunol Res. 2015;61(1-2):53-62. doi:10.1007/s12026-014-8561-9 10. Tomaras S, Goetzke CC, Kallinich T, Feist E. Adult-onset Still’s disease: clinical aspects and therapeutic approach. J Clin Med. 2021;10(4):733. doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040733 11. Ma Y, Meng J, Jia J, et al. Current and emerging biological therapy in adult-onset Still’s disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;60(9):3986-4000. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab485