![Desktop: [Left] Girl contemplating the luck her stuffed ladybug could bring her. [Right] Woman contemplating the luck her four-leaf clover necklace could bring her.](https://usim.beprod.ilarishcp.com/sites/ilarishcp_com/files/styles/hero_full_width_width_2560/public/2024-09/stills-disease-criteria-hero-image-d.jpg?itok=KK4ct3Zd)
Mechanism of Disease
Not an actual patient. Individual results will vary.
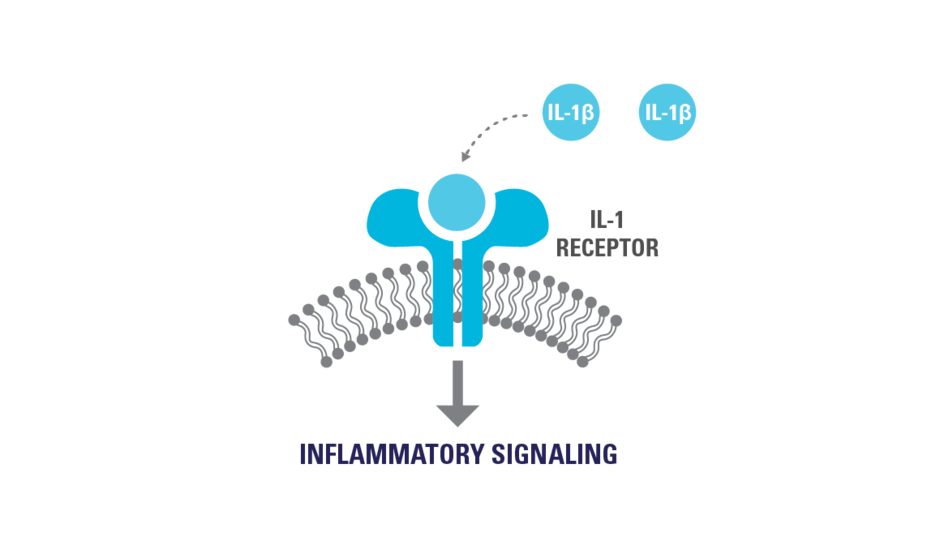
IL-1β is a critical driver of autoinflammatory disease1-4
Autoinflammatory diseases have a different pathogenic profile than autoimmune diseases1-6
| Autoinflammatory Diseases | Autoimmune Diseases |
| Key drivers: IL-1 β, IL-6, IL-18, and TNF | Key drivers: 1FN-y and IL-17 |
IL-1β is primarily induced and actively produced by immune cells under disease conditions7,8
In certain autoinflammatory diseases, there is an excessive release of activated 1L-1β.2,4,9,10
This overabundance can1,2,4,8-10:
- Cause an inflammatory cascade
- Trigger a feedback loop, inducing the production of even more IL-1β
The inflammatory cascade in PFS can drive fever and systemic inflammation1,4,11-12